How to Properly Add Tax to a Price: A Complete Guide for 2025
Understanding how to add tax to a price is crucial for both consumers and businesses alike. This complete guide provides you with the knowledge to effectively calculate, manage, and implement tax calculations, ensuring compliance and transparency in every transaction. As we navigate complex tax laws and evolving financial regulations in 2025, mastering the principles of pricing and taxation will empower you in making informed financial decisions.
Understanding Tax Rates
Before diving into the process of calculating tax on price, it’s essential to understand the different types of tax rates that may apply to your purchases or sales. Tax rates can vary based on jurisdiction, the nature of the goods or services being sold, and may even change with time. Most commonly, you’ll encounter sales tax, VAT, and service tax. Businesses must stay updated on local tax laws to ensure compliance, avoiding potential penalties. A solid understanding of these concepts will aid in creating a robust pricing strategy with tax.
Types of Tax Rates
Tax rates can be broadly categorized into three types: fixed, variable, and reduced. A fixed rate tax remains constant irrespective of the product price. Variable rates, however, adjust based on the price or type of goods. Additionally, certain items may qualify for reduced tax rates, offering savings and influencing consumer choice. Knowledge of these types helps in determining the right price plus tax when making pricing decisions.
Sales Tax Regulations
In the United States, for example, sales tax laws vary dramatically from state to state. Understanding where your business operates and sells will guide you in calculating effective tax rates. Some states exempt certain goods from sales tax, while others may have multiple tax jurisdictions applying different rates. Always check the latest local tax rules to ensure you’re adhere to current regulations.
Calculating Tax on Price
Calculating tax on price is fairly straightforward once you understand the basic tax formula for prices. Let’s explore a tangible method for finding the total cost by including tax, creating clarity around total cost with tax.
Basic Tax Calculation Steps
To effectively calculate tax on price, you can follow a simple algorithm:
1. Identify the price before tax.
2. Determine the applicable tax percentage.
3. Multiply the original price by the tax rate.
4. Add this value to the original price to find the total.
For instance, if a product costs $100, and the tax rate is 5%, the calculation would be as follows: $100 x 0.05 = $5. Therefore, the total price including tax would be $100 + $5 = $105.
Examples of Tax Calculation
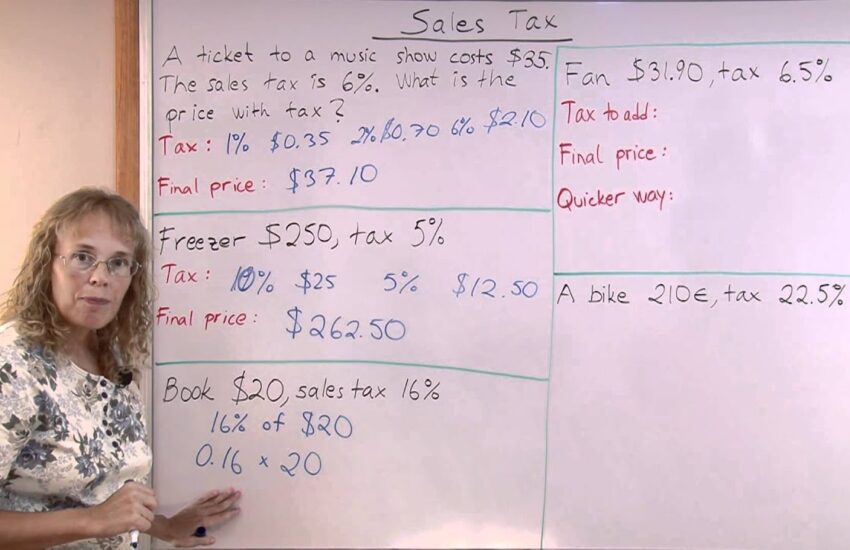
Let’s consider two common scenarios with different tax implications. In the first example, you’re purchasing a simple item with a direct sales tax. A book priced at $20 with a 6% sales tax would result in the following:
1. Tax amount: $20 x 0.06 = $1.20
2. Total price: $20 + $1.20 = $21.20
In another instance, consider purchasing dining services at a restaurant priced at $50 before tax. If the service tax is 8%, you’d have:
1. Service tax amount: $50 x 0.08 = $4
2. Total amount due: $50 + $4 = $54
Best Practices for Adding Tax
When managing pricing and taxation, businesses should establish a clear policy on how to calculate tax that aligns with their overall operational strategy. Incorporating these best practices into routine calculations can help in maintaining transparency with consumers.
Electing Tax-Inclusive Pricing
Using tax-inclusive pricing means incorporating tax into the displayed price rather than adding it at checkout. This method simplifies transactions for customers and communicates clarity about overall spending. Businesses can implement such strategies effectively by ensuring they correctly adjust the pricing formula to encompass applicable tax percentages.
Understanding Tax Obligations
Businesses must equip themselves with knowledge about their tax obligations. This includes understanding items that are taxable versus non-taxable, local tax rules, and maintaining accurate records to prepare for tax reporting requirements. Delaying action on tax matters can lead to fines and possible endangerment of business operations.
FAQ
1. What is the best way to manage tax on digital goods?
Tax codes for digital goods can vary significantly across jurisdictions. It’s crucial to research local regulations surrounding pricing digital goods with tax. Implement systems that automatically apply the correct tax rates based on the customer’s location for effective tax handling for business.
2. How can I ensure compliance during sales tax calculations?
Keeping up-to-date with the latest sales tax regulations may involve using tax calculation software or consulting with a tax professional. It’s important to regularly review changes in sales tax laws to maintain compliance and avoid legal complications.
3. Are there tax exemptions for any items or services?
Yes, often non-taxable items include food, medicine, and educational materials depending on the jurisdiction. It’s vital to identify these exceptions to avoid miscalculating taxes on purchases. Ensure your team understands what’s considered taxable versus non-taxable according to local tax rules.
4. How do I recover tax on taxable purchases?
You may be eligible for refunds of sales tax on returns or for certain business expenses. Familiarize yourself with your tax assessment process to ensure you’re correctly filing for recoverable taxes at the time of transaction processing.
5. Can adding VAT affect the sales price significantly?
Adding VAT can indeed impact the final sales price, particularly in markets where the VAT is high. Businesses must understand the implications of adding VAT to a price, as this will alter consumer perceptions and potentially affect overall sales.
6. What strategies can I employ to optimize my pricing with tax?
To ensure your pricing remains competitive while complying with tax standards, consider implementing dynamic pricing with tax or adjusting your product prices slightly lower to accommodate tax implications. This strategy balances consumer expectations with overall profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding various tax rates and their implications is critical for accurate pricing.
- Calculating tax on price is straightforward; apply the tax rate to the pre-tax figure.
- Employing tax-inclusive pricing promotes transparency and helps manage customer expectations.
- Stay informed about local sales tax regulations to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
- Consult with tax professionals or use software to streamline tax calculations and reporting.
By mastering the above principles on how to add tax to a price, consumers and businesses can navigate the complexities of taxation with confidence. For additional resources on tax calculations and their implications, visit this link or find comprehensive information here.