How to Properly Enable Virtualization in BIOS for Better Performance in 2025
Enabling virtualization in your computer’s BIOS settings can significantly enhance performance, especially if you utilize virtualization technology for running virtual machines or software applications. Many users are unaware of how to modify their BIOS configuration to enable this critical feature, which can unlock diverse capabilities in virtualization applications like VMware, VirtualBox, and Hyper-V. In this guide, we will walk through the steps to properly enable virtualization, enhancing your computing power for various tasks ahead in 2025.
Understanding Virtualization Technology
Virtualization technology allows a single processor to host multiple virtual environments, improving resource allocation and increasing efficiency. **Hardware virtualization** like Intel VT-x or AMD-V enables the CPU to run virtual machines more effectively, which can result in a dramatic increase in responsiveness for tasks such as gaming, software development, or running multiple operating systems simultaneously. In modern computing, utilizing these features necessitates changes in the **BIOS configuration** as they are not automatically enabled by default. Properly **enabling virtualization** opens doors to innovation in your desktop or server environments.
What is Virtualization Technology?
Virtualization technology refers to the creation of a digital version of physical resources, such as servers, storage, and networks. This technology operates by separating an operating system from the underlying physical hardware, thus allowing multiple operating environments to exist concurrently on a single physical machine. It can be beneficial for developers, businesses, or even casual users looking to optimize their system performance. Proper configuration of the motherboard BIOS to support virtualization features is essential for effective CPU virtualization, making it a critical aspect of any system setup.
Benefits of Enabling Virtualization
Enabling virtualization comes with several advantages. Key benefits include improved **virtualization performance** and efficiency in resource usage. By running multiple operating systems and applications concurrently, users can leverage the full potential of their CPU without compromising speed or performance. This helps in multitasking scenarios or applications that require high computational power, such as complex simulations or software development environments. Additionally, utilizing **virtualization in Windows** or other operating systems allows for seamless software testing and debugging, critical in today’s evolving tech landscape.
Common Applications of Virtualization Technology
Virtualization technology serves many practical purposes, such as developing and testing software in a controlled environment. Popular virtualization applications include VirtualBox, VMware, and Hyper-V, allowing users to create virtual machines and run different operating systems. In enterprises, virtualization often supports server consolidation, resulting in reduced hardware costs and improved efficiency. For developers, accessing virtualization options can create robust systems for testing and deployment, thus streamlining workflow processes significantly.
Steps to Enable Virtualization in BIOS
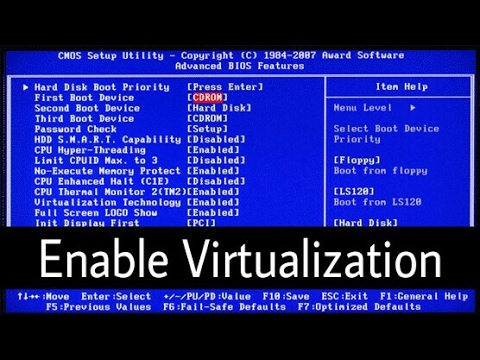
To activate **virtualization features** in BIOS, you must first access the BIOS menu, which can be done during the system boot-up phase. Find the appropriate BIOS access key for your computer’s manufacturer, usually displayed on the screen as you turn on the machine (such as F2, Delete, or Esc). Ensuring you **correctly access BIOS** will permit you to navigate through the **BIOS menu** where you can enable virtualization support.
Accessing the BIOS Menu
To enable virtualization, the initial task is to reboot your computer and press the appropriate **BIOS access keys** immediately after powering on. Each manufacturer may have a different access method, so referring to your motherboard manual can provide clear instructions on entering the BIOS interface. Within this interface, navigate carefully through the various menu options to locate settings related to virtualization. Most often, you’ll find “Virtualization Technology,” “Intel VT,” or “AMD-V” located under **CPU settings** or in the **Advanced Setup** section.
Navigating BIOS Settings for Virtualization
Once you’ve accessed the BIOS configuration, look under the advanced BIOS settings tab. The option to enable CPU virtualization should be clearly labelled. Select this option and change the setting from “Disabled” to “Enabled.” Make sure to save your changes by utilizing the save settings option before exiting. If available, you may also need to check your **BIOS firmware** for the latest updates which could provide additional virtualization options. This proactive step will ensure that the performance enhancements systems take advantage of the latest technologies available in **hardware virtualization**.
Finalizing BIOS and System Configuration
After enabling virtualization in BIOS, exit the menu, allowing your system to reboot. It’s crucial to enter your operating system’s settings and ensure that virtualization assist features are correctly installed or configured, especially if you plan to use applications like VirtualBox or VMware. You may want to review any software-specific settings to ensure they’ve recognized enabling virtualization. There are some common **virtualization troubleshooting** tips that could assist you if, upon booting back into your OS, you find performance doesn’t seem improved or virtualization appears disabled.
Optimizing Performance after Enabling Virtualization
The next step involves optimizing system resources after enabling virtualization. These tweaks ensure that your system runs as effectively as possible given the new settings. Proper configuration of your **virtualization applications** alongside your BIOS settings will enhance overall performance, particularly when running resource-heavy applications in virtual machines.
Configuring Virtual Machines
Once virtualization is enabled in your BIOS and you’ve rebooted your machine, the next crucial step involves configuring the settings in your chosen virtualization software. For instance, in VirtualBox, you would want to reserve adequate RAM and assign the correct number of CPU cores to your VM instances. Pay attention to the **performance options** presented within your virtual environments to ensure optimal allocation of resources. Essentially, sorting these settings maximizes what virtualization can do for your system.
BIOS Settings for Improved Virtualization Performance
In addition to enabling virtualization, you can further enhance your system’s performance by adjusting other **BIOS settings**. Consider the **BIOS memory settings** to allocate the necessary resources towards virtualization tasks. Most virtualization software will benefit from increased memory and processing capability; thus, adjusting these allow smoother VM operations. Also, pay attention to settings like PCIe virtualization support if your computer setup includes resources that would benefit from improved connectivity.
Monitoring Virtualization Performance
Post-setup monitoring is vital. Observe how well your system handles virtualization tasks, checking for signs of instability or lag, which might indicate issues with configuration. Application logs or system monitoring tools can help track performance trends. This step contributes significantly to maintaining optimal functioning and addresses potential issues as they arise before they impact your productivity or efficiency. Utilize established methodologies or software tools to thoroughly analyze and refine your setup.
Conclusion
In summary, enabling virtualization in your BIOS settings is a powerful method to optimize your system for enhanced performance in 2025. Following the steps outlined above ensures that you can properly set up and leverage the benefits of virtualization technology offered by your CPU. It’s imperative to familiarize yourself with your system’s BIOS configuration and the effects of virtualization to ensure you maintain a well-functioning virtual environment, especially if engaging in intensive tasks or utilizing programs like VMware or VirtualBox. Always reassess your BIOS settings to conform to any changes in your system usage to keep your performance at its peak.
Key Takeaways
- Access the BIOS using the correct keys upon booting up your computer.
- Enable virtualization features like Intel VT or AMD-V to unlock better performance.
- Make sure to save changes in the BIOS before exiting and rebooting.
- Optimize virtual machines by adjusting memory and CPU core allocation.
- Continuously monitor performance to refine settings further for the best virtualization outcomes.
FAQ
1. How do I know if virtualization is enabled on my computer?
You can check by accessing the Task Manager on Windows. In the Performance tab under CPU, it will state whether ‘Virtualization’ is enabled or disabled. If disabled, you may need to enable it in the BIOS settings.
2. What are the common BIOS access keys?
The most common access keys for BIOS include F2, Delete, Esc, and F10. The exact key may depend on your computer or motherboard manufacturer, so consult your manual if uncertain.
3. What should I do if virtualization is not available in BIOS?
First, ensure your CPU supports virtualization by checking the manufacturer’s specifications. If it does support it but is still unavailable, a BIOS update could potentially add this option.
4. Can enabling virtualization negatively impact my system’s performance?
While enabling virtualization should enhance performance for specific applications, in rare cases, it may introduce slight overhead. Ensure your system resources are adequate to avoid any potential performance degradation.
5. Is it necessary to reset BIOS after enabling virtualization?
No, it is not usually necessary to reset the BIOS after making changes. Simply saving the changes upon exit will allow the new virtualization settings to take effect upon the next system start-up.