“`html
Effective Ways to Determine Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in Atoms in 2025
Understanding the composition of atoms forms the foundation of chemistry. Atoms consist of three fundamental particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. This article will guide you on how to find protons, how to find neutrons, and how to find electrons in various elements, providing practical insights and modern methodologies integral to atomic theory.
Understanding Atomic Structure
Atomic structure is pivotal to grasp the intricate relationships between protons, neutrons, and electrons. The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom, and it is crucial for identifying elements in the periodic table. Moreover, the mass number, which is the total number of protons and neutrons, helps in understanding isotopes of elements. For instance, a carbon atom has an atomic number of 6, meaning it contains 6 protons and typically 6 neutrons, contributing to a common carbon isotope.
Protons in an Atom
Protons carry a positive charge and significantly influence an atom’s elemental identity. To ascertain the number of protons in an atom, refer to its atomic number on the periodic table. For example, the element oxygen has an atomic number of 8, indicating it contains 8 protons. This directly correlates to its chemical properties and reactivity. Knowing the number of protons is essential not only in chemistry but also in subatomic particle physics and fundamental particle interactions.
Neutrons in an Atom
Neutrons are electrically neutral subatomic particles found within the atomic nucleus. They play a crucial role in adding mass to an atom without affecting its charge. To find the number of neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the mass number. For instance, if an element has a mass number of 14 (like carbon-14), it would contain 8 neutrons (14 – 6 protons). Understanding the role of neutrons is essential, especially when studying isotopes, which have varying numbers of neutrons.
Electrons in an Atom
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom in electron shells. The typical number of electrons in a neutral atom matches the number of protons. For example, with a neutral carbon atom having 6 protons, it also has 6 electrons. This balance of charges maintains the electrical neutrality of the atom. Understanding the electron configuration is vital for predicting how atoms will bond in chemical reactions.
Calculating Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Calculating these subatomic particles follows straightforward methodologies, particularly when utilizing the periodic table as a tool. By verifying atomic and mass numbers, one can efficiently deduce the counts of each particle.
Methods for Calculating Protons
To calculate protons in any given atom, simply refer to the atomic number listed in the periodic table. This straightforward approach is an effective way to identify the elemental nature of substances in your experiments.
Techniques for Finding Neutrons
Finding neutrons requires you to first identify the atom’s mass number and atomic number. The formula is as follows: Neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number. This calculation helps you understand various isotopes of an element and their stability. For example, the two common isotopes of hydrogen are deuterium (one neutron) and tritium (two neutrons).
Identifying Electrons
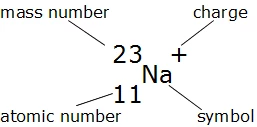
Finding electrons is simplified in neutral atoms where the counts of electrons equal protons. However, in charged ions, adjustments may be necessary. For example, sodium (Na) ordinarily has 11 electrons, but as a positively charged ion (Na+), it has 10 electrons after losing one during ionization.
The Role of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in Chemical Properties
The interactions between protons, neutrons, and electrons govern not only elemental identity but also their chemical properties, stability, and reactions. For example, the number of protons determines how atoms bond with others, leading to the development of compounds.
Interactions Between Atomic Particles
Understanding the relationships between these particles is fundamental in chemistry. Both protons and neutrons form the nucleus, while electrons occupy cloud-like regions surrounding the nucleus. This arrangement underpins the stability and reactivity of elements. Elements with similar atomic structures exhibit similar chemical properties, a concept summarized in the periodic trends.
Exploring Isotopes
Isotopes are variants of elements that have the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons. This knowledge enhances your understanding of atomic mass and behavior during chemical reactions. For instance, the commonly known isotopes of carbon (carbon-12 and carbon-14) play critical roles in various scientific applications ranging from dating archaeological finds to understanding biological processes.
Conclusion on Atomic Composition
Understanding the structure and interactions of protons, neutrons, and electrons is fundamental to both the field of chemistry and our broader understanding of matter. By mastering these concepts, you will greatly enhance your ability to predict and explain various chemical phenomena.
FAQ
1. How do I identify protons in an atom?
To identify protons, locate the atomic number on the periodic table. The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom. For instance, gold has an atomic number of 79, so it contains 79 protons.
2. What is the significance of neutrons in an atom?
Neutrons play a vital role in maintaining the stability of an atomic nucleus. Their presence helps balance the positive charges from protons, preventing the nucleus from repelling itself. They also contribute to the mass of the atom.
3. How can I calculate electrons in an atom when it is ionized?
In ionized atoms, the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons. For a positively charged ion, subtract the charge from the proton count. For a negatively charged ion, add the charge to the proton count to find the total electron count.
4. What is the impact of atomic number and mass number on atoms?
The atomic number defines the element by indicating the number of protons, while the mass number provides total protons and neutrons. This fundamental information is crucial for isotope discovery and understanding atomic stability.
5. How do subatomic particles influence chemical reactions?
The arrangements and interactions of protons, neutrons, and electrons determine how atoms bond and react chemically. Charged electrons participate significantly in chemical bonding, making their distribution crucial for chemical properties and reactions in matter.
6. Can you explain the difference between elements and isotopes?
Elements consist of atoms with the same number of protons, while isotopes are variations of a single element with differing numbers of neutrons. This difference impacts the atomic mass and certain physical properties of the isotopes.
7. Why is it important to understand atomic charge and stability?
Understanding atomic charge and stability is essential for predicting how atoms interact in chemical reactions. It determines bonding behavior, reactivity, and the overall integrity of molecules across various chemical contexts.
“`