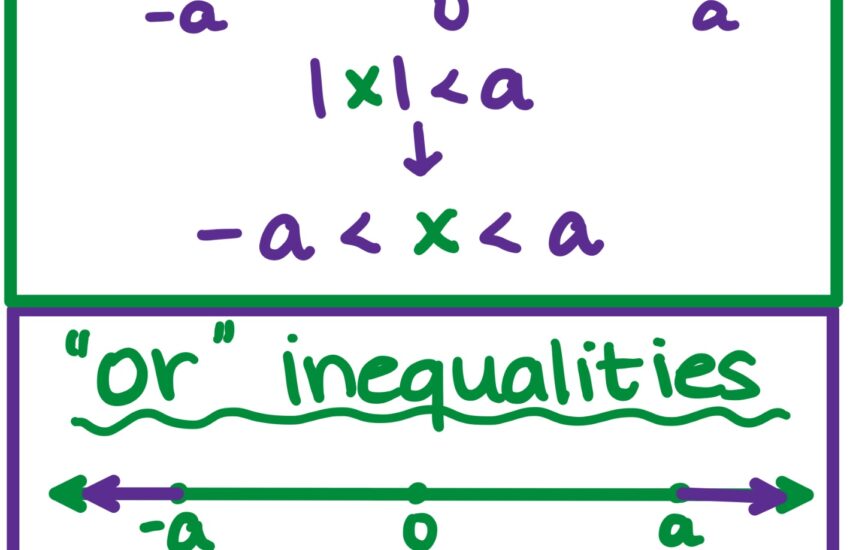How to Properly Find Absolute Value
Understanding Absolute Value
The concept of **absolute value** is one of the foundational principles in mathematics, pertinent to various domains such as algebra, geometry, and statistics. At its core, the absolute value of a number reflects its **numerical distance** from zero, irrespective of direction. In mathematical notation, the absolute value of a number \(x\) is denoted as \(|x|\). For example, both \(|3|\) and \(|-3|\) equal 3, illustrating that absolute value strips away any negative signs, focusing solely on magnitude. This **absolute value function** encourages a deeper analysis of numbers and their relationships, making it essential for understanding algebra and solving inequalities.
What is Absolute Value?
The **absolute value definition** can be articulated simply: it measures how far a number is from zero on a number line. For non-negative numbers, the **absolute value** is the number itself, while for negative numbers, it is the positive counterpart. This duality explains why learning how to calculate absolute value is critical. It can be encountered frequently, for instance, when solving **absolute value equations** that require isolating the variable. An example of such an equation is \(|x| = 4\), where two solutions, \(x = 4\) and \(x = -4\), emerge. By using the **absolute distance** concept, we can visualize these values effectively, aiding in geometric interpretations in higher math.
Absolute Value Notation and Properties
When navigating through mathematical expressions, understanding **absolute value notation** and its properties is paramount. Notably, the three primary properties of absolute value are: **absolute value of a product** equals the product of the absolute values, the **absolute value of a quotient** equals the quotient of the absolute values, and the **absolute value of a sum** could be less than or equal to the sum of the absolute values. Real-world applications of these properties often show in physical contexts—like calculating distances and measuring calculations in fields such as physics and engineering, where finding the absolute value plays a crucial role in the accuracy of results.
How to Calculate Absolute Value
Calculating absolute value can seem straightforward, but knowing various methods can enhance efficiency. The most direct approach uses the **absolute value function**; simply employ the notational framework to derive results. If using a calculator, an **absolute value calculator** will expedite the process, especially when working with complex equations or larger datasets. In programming, the concept translates seamlessly into functions across languages, allowing developers to leverage this **absolute value in programming** for efficient code solutions.
Practical Techniques for Determining Absolute Value
One practical method for determining absolute values is through the logical breakdown of the scenarios: if a number is greater than or equal to zero, the output is the number itself; if it’s less than zero, output the negative of the number. This can be illustrated with how to solve absolute value equations: consider the equation \(|x + 2| = 5\). We can separate it into two parts: \(x + 2 = 5\) and \(x + 2 = -5\), leading to solutions of \(x = 3\) and \(x = -7\). This systematic approach aids in both **absolute value addition** and **absolute value subtraction**, allowing clear identification of roots in complex structures.
Graphing Absolute Values
Understanding the graph of the absolute value function gives insights into its innate behavior. The graph’s **absolute value graph** appears as a V-shape, due to the fact that for every input there is a positive and negative output. The vertex represents the point of minimum value, occurring at coordinates of the related function’s base point. For instance, with \(y = |x|\), the vertex is at the origin (0,0). Graphs serve not only to represent functions but also to visualize **absolute values and inequalities**, clarifying relations between different values in applied mathematics contexts.
Applications of Absolute Value
**Absolute value applications** are ever-present in both theoretical math and real-world scenarios. In statistics, the absolute value can articulate variations and discrepancies crucial for data analysis. Moreover, in the field of physics, the concept helps contextualize forces and displacements, wherein calculations often regard not just the values, but their absolute significance. Recognizing the **absolute value in geometry** allows for a clearer perception of spatial relationships and metrics, vital for studies incorporating analytics.
Absolute Value and Inequalities
In dealing with **absolute value inequalities**, one must recognize the critical connection between values that demonstrate bands of numbers. Consider the inequality \(|x| < 3\): it translates to \(-3 < x < 3\). Using such transformations aids in revealing solution sets efficiently while maintaining logical rigor in broad problem-solving scenarios. This illustrates the systematic reduction often necessary in inequalities and supports the rules governing absolute values in mathematics.
Real Life Examples of Absolute Value
Absolute value applications extend into real-life contexts, particularly when one evaluates change and distance. For instance, when measuring the altitude of an aircraft in relation to sea level, the **absolute value of negative numbers** contributes to understanding total altitude. Moreover, in finance, evaluating profit or loss can employ absolute values to underscore the amounts being assessed without negative implications. Yet another area is in programming, where controlling values through function transformations allows developers to maintain integrity in data—assessing input efficacy without reference to input directionality.
Key Takeaways
- Absolute value represents the distance of a number from zero.
- Understanding the properties and rules of absolute values improves problem-solving skills.
- Absolute value calculations are applicable across various domains, including finance and physics.
- Graphical representation aids in comprehending the relationships and behaviors of absolute values.
- Absolute value is essential for managing inequalities and complex equations.
FAQ
1. What is the absolute value of a negative number?
The **absolute value of negative numbers** translates to the corresponding positive value. For instance, the absolute value of \(-5\) is \(|-5| = 5\). This indicates how far the number \(-5\) is from zero on the number line, fully embodying the concept of **absolute distance**.
2. How do absolute value inequalities differ from absolute value equations?
While **absolute value equations** equate an absolute value expression to a number, absolute value inequalities express relationships involving less than or greater than. For example, \(|x| > 2\) would lead to two ranges of solutions (\(x 2\)), demonstrating the broader sets yielded by inequalities as opposed to the singular outcomes found in equations.
3. Can you provide an example of an absolute value application in real life?
An example can be found in geometry, where the **absolute value concept** assists in calculating distances between points on a coordinate plane. If one point lies at (3, 4) and another at (1, 1), the distance between them can be evaluated using the **absolute distance** formula, factoring in varying x and y coordinates to arrive at a geometric solution.
4. How do I use an absolute value calculator?
Using an **absolute value calculator** is straightforward; input the number or expression whose absolute value you wish to find, and the calculator computes the result. This tool is handy for resolving complex calculations quickly, particularly when managing larger datasets in mathematical or programming applications.
5. What are some common properties of absolute values?
There are several core **absolute value properties** to recognize: the absolute value of a product is the product of absolute values, the absolute value of a sum does not exceed the sum of the absolute values, and the absolute value of zero is zero itself. These rules dictate how to manipulate and resolve equations involving absolute values, creating a foundation for deeper mathematical explorations.
6. How are absolute values applied in statistics?
In statistics, absolute values are utilized for measuring deviations from the mean to assess the **absolute distance** of data points, aiding in the formation of measures like the mean absolute deviation. This underscores the importance of distance and how it reflects deviations in datasets, helping derive accurate interpretations of variability.
7. In what ways can I visualize absolute value?
**Visualizing absolute values** often employs the number line to represent values. A **number line and absolute value** illustration showcases distances clearly, subdividing values above and below zero while emphasizing differences regardless of sign, which boosts understanding of how absolute values function visually.