How Long Does It Take to Fly to the Moon: A Complete Guide for Your 2025 Journey
Planning to embark on a journey to the Moon in 2025? Understanding the logistics and **moon flight duration** is essential for an unforgettable experience. This detailed guide will help you navigate the complexities of lunar travel, including preparation time, scheduling, and factors impacting your **time to reach the moon**. Let’s explore the world of **flying to the moon**!
Understanding Moon Flight Duration
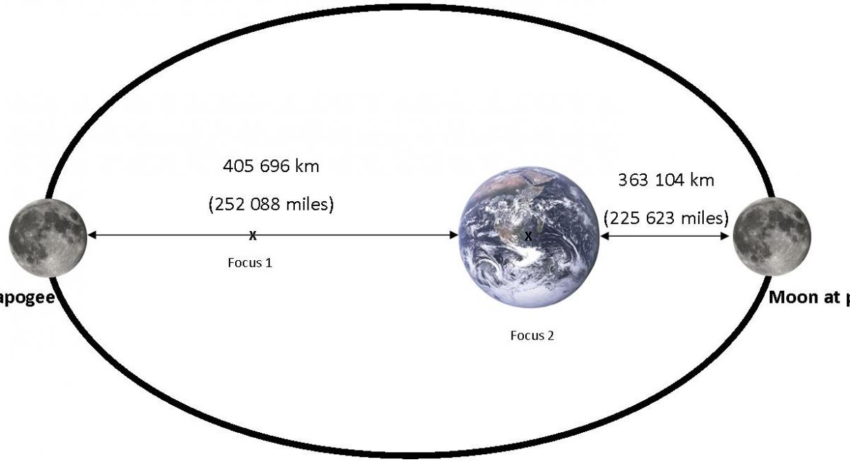
The **moon flight duration** varies significantly based on the type of mission and spacecraft used. Typically, the average **flight time to the moon** is around 3 days, depending on the launch vehicle and trajectory. For instance, the Apollo missions took approximately 72 hours to cover the distance of about 238,855 miles from Earth to the lunar surface. Understanding the **distance to the moon from Earth** and various mission designs can help set proper expectations for the **journey to the moon duration**.
Factors Affecting Moon Trip Duration
Several factors can influence the **lunar travel time**. The spacecraft’s trajectory, speed, and the propulsion systems employed play a pivotal role. For instance, traditional rockets like the Saturn V used during the Apollo missions had an average travel speed of roughly 3,500 kilometers per hour (about 2,200 miles per hour). In contrast, newer technologies aim for faster speeds, significantly reducing the average **time to the moon**. Also, mission objectives, whether for exploration or tourism, can affect the duration due to planned stops or orbital maneuvers.
Historical Context: Apollo Moon Landing Travel Time
The **Apollo moon landing travel time** set many benchmarks for future lunar expeditions. For example, the Apollo 11 mission took approximately 76 hours from launch to lunar orbit insertion. This historical data provides valuable insights into the expected **moon mission duration** for upcoming journeys. For travelers planning to fly to the moon, it’s crucial to learn from past missions while also considering advancements in technology that might shorten this duration.
Planned Lunar Flight Timings for Future Missions
As companies and space agencies prepare for the next wave of lunar missions, planned flight timings are taking shape. Future missions are expected to incorporate a variety of factors, from scientific objectives to **lunar travel logistics**. For example, potential lunar tourism ventures may see a slightly longer **moon expedition duration** due to scheduled pauses for activities. This preparation is essential for enhancing the traveler experience while balancing the required **preparation time for moon flight**.
Rocket Technology and Moon Travel
Evolution in **rocket technology for moon flights** has dramatically changed expectations for **lunar exploration**. Modern spacecraft design focuses on enhanced propulsion systems to reduce the **moon travel obstacles** inherent in earlier missions. For example, advanced engines are being developed that may dramatically speed up the **lunar flight time**.
Commercial Flights to the Moon
The advent of commercial space travel has opened up exciting possibilities for lunar expeditions. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are making strides in securing **flight permits to the moon**. While specific schedules are still in development, the anticipated time for **lunar tourism** may mirror historical contexts with enhancements to comfort and efficiency, ultimately contributing to the **economic benefits of lunar travel**.
Challenges of Lunar Exploration
Despite advancements, challenges persist in the form of **safety measures in moon travel** and the potential environmental impacts of **mining lunar resources** and expanding assault on the lunar surface. Addressing safety concerns while promoting sustainable practices is vital for long-term **lunar base establishments**. This balance is key as explorers and scientists prepare for **long-term space missions** aimed at establishing humanity’s presence on the Moon.
Moon Travel Logistics
Proper **moon travel logistics** are crucial for successful trips. This includes understanding the **lunar geography for travelers**, ensuring adequate preparation for the unique challenges of the Moon’s environment, and scheduling time efficiently. For example, accurately pinpointing lunar landing sites to avoid problematic terrains coupled with precise lunar **navigation mechanics** can heavily influence mission success.
Preparation and Training for Lunar Missions
Preparing for a trip to the moon includes rigorous **astronaut training** and understanding microgravity effects. The success of previous missions, such as the Apollo program, relied heavily on well-trained astronauts familiar with spacecraft systems and **lunar impact studies**. Upcoming missions may require similar preparation, emphasizing the importance of astronaut training in experiencing **space travel to the moon** safely.
Astronaut Training Essentials
A critical aspect of ensuring the success of a **manned moon mission time** involves comprehensive astronaut training. This can range from physical fitness to simulating **lunar landscape explorations**. Key parameters include preparing for reentry procedures, emphasizing **orbital insertion**, and understanding gravitational forces that come into play during different mission phases. Such preparation not only enhances survival rates and mission efficiency but encourages bold moon endeavors for scientific purposes.
Lunar Mission Objectives
Different missions have unique objectives, significantly influencing **moon travel capabilities**. Scientific missions focus on gathering lunar regolith samples, while tourism might prioritize exceptional experiences within the lunar habitat. During this preparation time, **considerations for traveling to the moon** must be meticulously developed to ensure credibility while capturing travelers’ imaginations.
Safety Measures in Moon Travel
The challenge of ensuring adequate **safety measures in moon travel** is paramount. From designing safe **lunar landers** to implementing propulsion systems able to withstand potential emergencies, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Any firm undertaking **moon mission protocols** must adhere diligently to safety standards and regulations regulated by international standards. Developing emergency protocols aids efficiency and ensures effective response to potential challenges during critical mission phases.
Key Takeaways
- The average **moon flight duration** is around 3 days, influenced by spacecraft technology and mission objectives.
- Understanding the **distance to the moon from Earth** is crucial for calculating travel time.
- **Rocket technology for moon flights** has evolved, paving the way for commercial lunar tourism.
- Preparation and **astronaut training** are essential for successful journeys to the Moon.
- Understanding **safety measures in moon travel** is vital to ensure the success of lunar missions.
FAQ
1. What is the distance to the Moon from Earth?
The average distance to the Moon from Earth is about 238,855 miles (384,400 kilometers). This distance varies slightly due to the elliptical shape of the Moon’s orbit but remains a crucial factor in understanding **moon flight duration** and logistics.
2. How fast do you travel to the Moon?
The speed of travel to the Moon can vary, but during the Apollo missions, the spacecraft achieved speeds of approximately 3,500 kilometers per hour (2,200 miles per hour). Advances in **spacecraft design** and propulsion technology may enhance **moon flight speed**, aiming for even shorter travel times in the future.
3. What are the main considerations for traveling to the Moon?
Key considerations include understanding **lunar travel logistics**, assessing safety measures, and addressing environmental impacts. Prior planning ensures adherence to protocols and enhances overall mission safety, drawing from lessons learned from historical missions.
4. How has rocket technology changed for future missions?
Modern advancements have led to improved propulsion mechanisms and new **rocket launches** that cater to commercial space travel. Innovations in **space exploration technologies** have made planning for effective lunar trips more efficient, focusing on safety and speed.
5. What are the anticipated outcomes of future lunar missions?
Anticipated outcomes of future lunar missions include expanded scientific knowledge through research and feasibility studies, paving the way for more consistent **lunar exploration** and tourism opportunities. Achievements in **moon travel capabilities** can lead to significant economic benefits through tourism and resource utilization.